What Is Communication Sciences and Disorders?
Jan 19, 2024
 Communication is the cornerstone of human interaction, allowing us to express thoughts,
feelings, and needs. However, due to communication disorders, the simple act of communication
can be fraught with challenges for millions of individuals worldwide. A multifaceted
field dedicated to addressing various communication challenges is Communication Sciences
and Disorders (CSD). CSD professionals treat speech, language, hearing, and swallowing
disorders or impairments, helping individuals form relationships, access education
and employment opportunities, and participate fully in society.
Communication is the cornerstone of human interaction, allowing us to express thoughts,
feelings, and needs. However, due to communication disorders, the simple act of communication
can be fraught with challenges for millions of individuals worldwide. A multifaceted
field dedicated to addressing various communication challenges is Communication Sciences
and Disorders (CSD). CSD professionals treat speech, language, hearing, and swallowing
disorders or impairments, helping individuals form relationships, access education
and employment opportunities, and participate fully in society.
Follow along as we delve deeper into what you need to become a Communications Sciences and Disorders graduate and explore the types of Communication Sciences and Disorders, salaries and job outlooks for CSD graduates, and more.
What Is a Communication Sciences and Disorders Degree?
A Communication Sciences and Disorders degree focuses on the study of the biological, physical, social, and linguistic aspects of human communication. This field covers the intricate details and scientific principles that underpin communication disorders such as speech, hearing, and language. Additionally, it equips individuals with the fundamental knowledge and practical experience necessary to assist those with communication impairments caused by genetic, developmental, neurological, or unknown conditions.
What makes Communication Sciences and Disorders invaluable is the prevalence of communication disorders in approximately 40 million Americans. Professionals in this field are crucial in improving communication and quality of life for individuals with disorders. They can assess, diagnose, and treat various communication disorders across the lifespan from childhood to adulthood.
Qualifications Needed To Become a Communication Sciences and Disorders Graduate
Becoming a Communication Sciences and Disorders graduate requires a combination of academic coursework and clinical training to practice professionally in the field.
Education
The first step to pursuing a graduate degree in CSD is completing a bachelor's degree in Communication Sciences and Disorders. While your bachelor's CSD degree provides you with the foundational knowledge and skills about the nature of human communication, it's a pre-professional degree, so you'll need additional training and education to practice in the field. This undergraduate degree serves as a stepping stone to a career as either a speech-language pathologist or audiologist.
Once you have completed your bachelor's degree, you will need to pursue a master's degree in Communication Sciences and Disorders. Our graduate program is designed to prepare you for a career in speech-language pathology through comprehensive coursework with an emphasis on clinical training. Upon completion of the program, you will be eligible for the Certificate of Clinical Competence in Speech-Language Pathology.
Experience
Practical experience is highly valuable in preparing you to meet the demands of your profession and enhancing your skills and knowledge in your field. By gaining hands-on experience, you will learn to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world settings and develop your clinical skills. As an aspiring CSD graduate, some of the clinical or practical experiences that can be highly beneficial for you include:
- Internships: Seeking internship opportunities allows you to work alongside therapists with individuals and their families and learn more about evaluating and treating patients. You can intern in hospitals, rehabilitation centers, private practices, or public schools.
- Volunteer work: Volunteering allows you to make meaningful contributions to the communities while learning more about the profession. You can volunteer in settings such as preschools and k-12 schools, hospitals, private practices, nonprofits, government agencies, community centers, and more.
- Research experience: Engaging in research allows you to enhance your academic experience and develop research skills in areas of interest. Moreover, you'll learn more about the methodologies and techniques utilized in research.
Types of Communication Sciences and Disorders
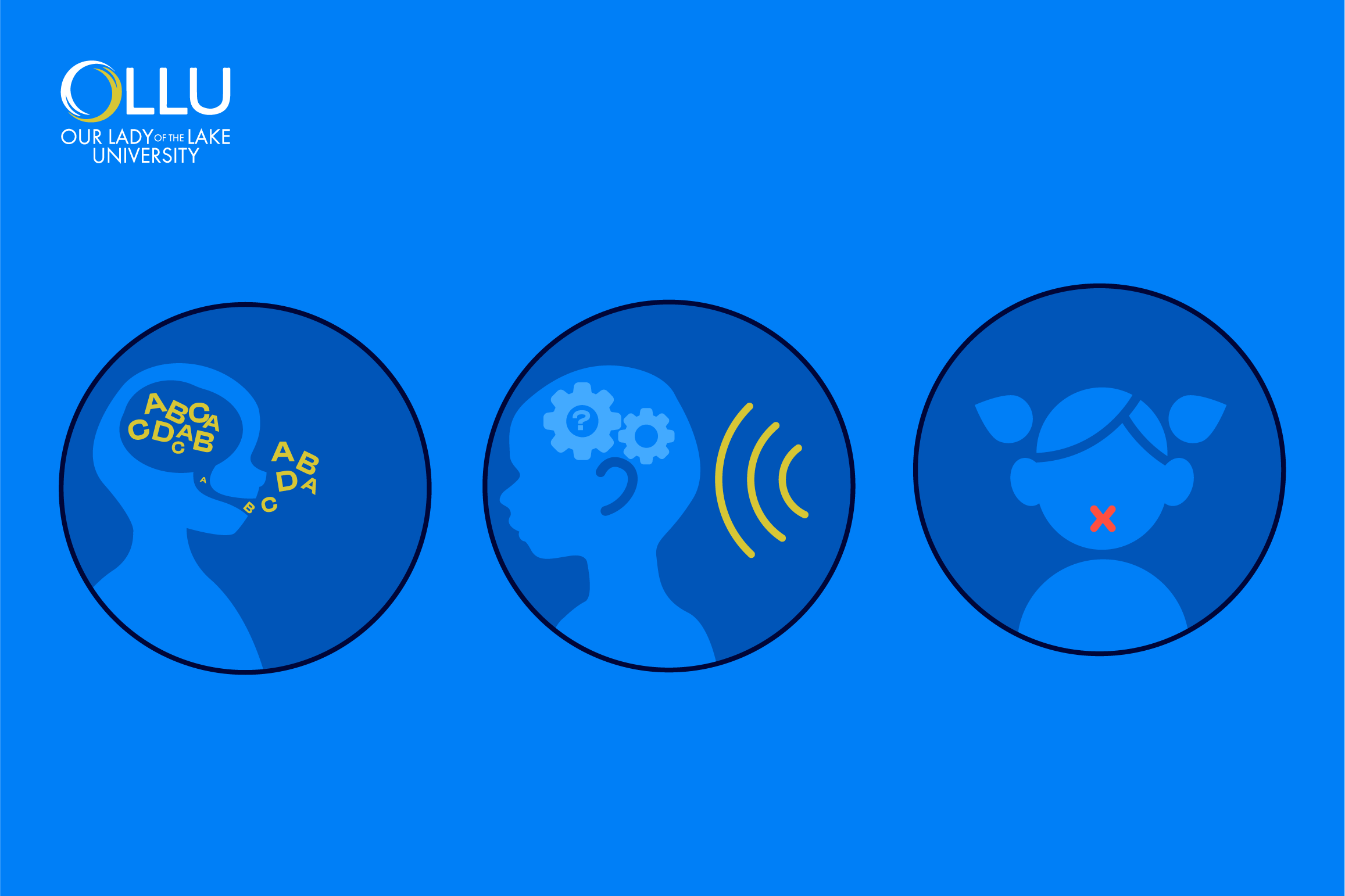 Communication Sciences and Disorders encompass various types of disorders, each presenting
unique obstacles that can impact interaction and overall quality of life. In the following
sections, we will explore each type of disorder, its characteristics, and potential
interventions.
Communication Sciences and Disorders encompass various types of disorders, each presenting
unique obstacles that can impact interaction and overall quality of life. In the following
sections, we will explore each type of disorder, its characteristics, and potential
interventions.
Articulation disorders
Articulation refers to the process we go through to produce sounds, syllables, and words. In some conditions, individuals cannot form particular sounds correctly or make certain sounds. These conditions are known as articulation disorders, and they entail the inability to correctly produce speech sounds due to the imprecise placement, pressure, speed, timing, or the flow of movement of the lips, tongue, or throat. Common articulation disorders include:
- Omission: Leaving certain sounds out of the speech entirely, e.g., never using "sc" in "school."
- Substitution: Substituting one sound for another, e.g., using "w" instead of "r."
- Addition: Adding syllables or sounds to words, e.g., "puh-lay" instead of "play."
- Distortion: Changing a sound, e.g., when "s" sounds like "th."
Fluency disorders
Fluency refers to the smoothness, rate, and continuity of speech production. While everyone is disfluent at times, individuals with fluency disorders experience an interruption in the flow of speaking marked by atypical rate, rhythm, and disfluencies (such as repetition of words, syllables, and sounds).
The most common fluency disorders include:
- Stuttering: As the most common fluency disorder, stuttering refers to the interruption in the flow of speaking characterized by disfluencies such as repetitions of sounds, syllables, and words, prolongations of consonants, and the inability to initiate sounds.
- Cluttering: This type of disorder is characterized by a perceived rapid or irregular speech rate, maze behaviors, pragmatic issues, moments of dysfluency, atypical pauses, and language formulation issues.
Voice disorders
Voice disorders affect an individual's ability to speak clearly and refer to abnormalities in pitch, volume, or quality of the voice. The treatment of voice disorders can take either the direct or indirect approach. The direct approach focuses on manipulating voice-producing mechanisms to modify vocal behaviors and establish healthy voice production. On the other hand, the indirect approach focuses on changing the cognitive, psychological, physical, and behavioral environments in which voicing occurs through patient education and counseling.
Moreover, there are many types of voice disorders, including:
- Laryngitis: This disorder manifests as hoarseness and results from the swelling of vocal cords due to allergies or an upper respiratory infection.
- Vocal cord paresis: Because of a viral infection, stroke, or injury to a nerve, the vocal cords can be paralyzed, leading to a weak, breathy voice.
- Spasmodic dysphonia: It's caused by a nerve problem leading to the spasm of vocal cords, making the voice sound hoarse, tight, or quivery.
Language disorders
Language disorders refer to difficulties in conveying meaning through speech, writing, or gestures. These disorders can persist throughout the lifespan, and the symptoms may change. The main types of language disorders are:
- Receptive language disorder: This disorder refers to difficulty understanding words and/or sentences, following directions, and difficulty attending to the speech of others.
- Expressive language disorder: Contrarily, this disorder includes difficulty using the right words when talking, difficulty putting sentences together correctly, difficulty combining words to make sentences, and limited vocabulary.
Salary and Job Outlook
The CSD field offers promising career prospects, with opportunities for advancement and various career pathways, such as:
- Speech-language pathologist
- Audiologist
- Rehabilitation aide
- Behavioral therapist.
According to BLS data, the median annual wage for speech-language pathologists is $84,140 or $40.45 per hour. The lowest 10% of speech-language pathologists earn less than $56,370, whereas the highest 10% earn more than $126,680. The employment of speech-language pathologists is estimated to grow 19% from 2022 to 2032, with about 13,200 openings each year. Moreover, the top industries where speech-language pathologists work are:
- Nursing and residential care facilities
- Hospitals
- Offices of occupational, physical, and speech therapists and audiologists
- Educational services in local, state, and private settings.
On the other hand, the BLS reports an annual wage of $82,680 or $39.75 per hour for audiologists. The lowest 10% earn less than $56,990, and the highest 10% earn more than $120,380. Furthermore, the employment of audiologists is estimated to grow 11%, with about 900 openings each year in the 2022-2032 period. Employment trends show that the top industries where audiologists work are:
- Hospitals
- Educational services in local, state, and private settings
- Offices of physicians
- Offices of occupational, physical, and speech therapists and audiologists.
The Bottom Line
What makes pursuing a career in CSD worth it isn't just the high salary and job outlook. As a CSD professional, either as a speech-language pathologist or audiologist, you'll be able to break down communication barriers and address communication challenges, helping individuals connect with others and improve their quality of life.
So, whether you're considering a career in CSD or want to learn more about the educational requirements, we encourage you to explore this fascinating field further. Feel free to contact us for any additional information!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is CSD a hard major?
Although a major in CSD is rewarding, it can also be overwhelming. As a CSD student, you'll have to juggle a rigorous course load and clinical practical experiences. However, all the stress and all of the world as a CSD graduate will pay off, and in the end, you'll be able to work in some of the most rewarding jobs out there.
What does Communication Science do?
Communication Science and Disorders encompass various services to assess, diagnose, and treat various communication disorders. Moreover, CSD professionals develop personalized strategies tailored to address each patient's unique concerns.
Why should I study communication science?
Studying communication sciences and disorders provides the opportunity to develop specialized knowledge and skills in assessment and intervention and opens doors to rewarding careers dedicated to improving communication outcomes and quality of life for individuals with communication disorders.
What are the benefits of studying Communication Science?
One of the most important benefits of studying Communication Sciences and Disorders is that you'll be able to pursue diverse and fulfilling careers such as speech-language pathologists, audiologists, rehabilitation aides, and more. Furthermore, graduating with a CSD major allows you to impact the lives of individuals with communication disorders positively. And lastly, as CSDs are in demand, you'll benefit from the high compensation and job opportunities.