IT vs. Cybersecurity Degree: Which Is Right for You?
Oct 27, 2023

From the moment we wake up, we interact with technology in various forms. We check our phones for messages and news, use computers at work, utilize social media to stay connected and more. Technology plays a significant role in our lives and its influence only increases. Therefore, considering a career in technology and computers is a wise choice.
However, the multitude of options can be daunting. But no worries, we’re here to help you navigate between two key choices: IT and cybersecurity. Read on as we compare IT vs. cybersecurity, covering aspects such as curriculum, job prospects, essential skills and more. This way, you’ll be well-equipped to make an informed decision about your career journey in the technology field.
Understanding the Basics
The first step is to understand the fundamentals of IT and cybersecurity, including their core concepts. By familiarizing yourself with this information, you’ll be better equipped to determine which path aligns most closely with your interests and career aspirations.
IT
Information technology (IT) is a multidisciplinary field that revolves around using technology to store, retrieve, transmit and manipulate data or information for various purposes.
An IT degree program is designed to equip students with a broad range of knowledge and skills related to the effective management, utilization, and support of technology within various organizational contexts.
At the core of such degree programs stand:
- Computer Systems
- Hardware
- Software Development
- Programming
- Databases
- Data Management
Cybersecurity
On the other hand, cybersecurity is a specialized domain within computer science that focuses on the comprehensive understanding and practical application of techniques and strategies to secure digital assets and information systems from various cyber threats. At the core of cybersecurity lie the three fundamental principles represented by the CIA triad:
- Confidentiality ensures that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized individuals or systems. It involves mechanisms and protocols to prevent unauthorized access or disclosure of classified data.
- Integrity ensures data accuracy, consistency and trustworthiness throughout its lifecycle. It involves measures to detect and prevent unauthorized alterations or tampering of information.
- Availability guarantees that necessary information and systems are accessible and operational when required. It involves implementing measures to prevent or recover from disruptions, ensuring that critical services remain available.
Curriculum Differences
Next, we’ll go through the curricula for both fields. This exploration will allow for a detailed examination of the specific courses, subjects and areas of focus within each discipline.
IT
The curriculum of an IT degree program is designed to equip you with a diverse set of skills and knowledge crucial for success in today’s technology-driven world through a wide range of courses focused on core concepts and others exploring specialized topics.
Some of the courses you can typically expect to see in any IT program include:
- Computer Systems and Hardware
- Operating Systems
- Business Intelligence and Data Analytics
- IT Risk Management
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in IT
- Web Development and Design
- Software Development and Programming
- Networking and Communication
- Databases and Data Management
- Cloud Computing
Cybersecurity
Curricula in cybersecurity programs are specifically designed to provide you with specialized training across various areas through carefully selected courses focused on the expertise and knowledge required to work in cybersecurity.
For example, within our Master of Science degree in Cybersecurity and Cybersecurity Certificate, you will explore a range of courses, such as:
- Applied Cryptography
- Computer and Network Security
- Computer Programming Logic and Design
- Networking Technology
- Introduction to Malware Analysis
- Database Analysis and Design
- Information Systems Analysis and Design
- Networking Design and Implementation
- Systems Project
- Intrusion Detection and Response
Career Opportunities
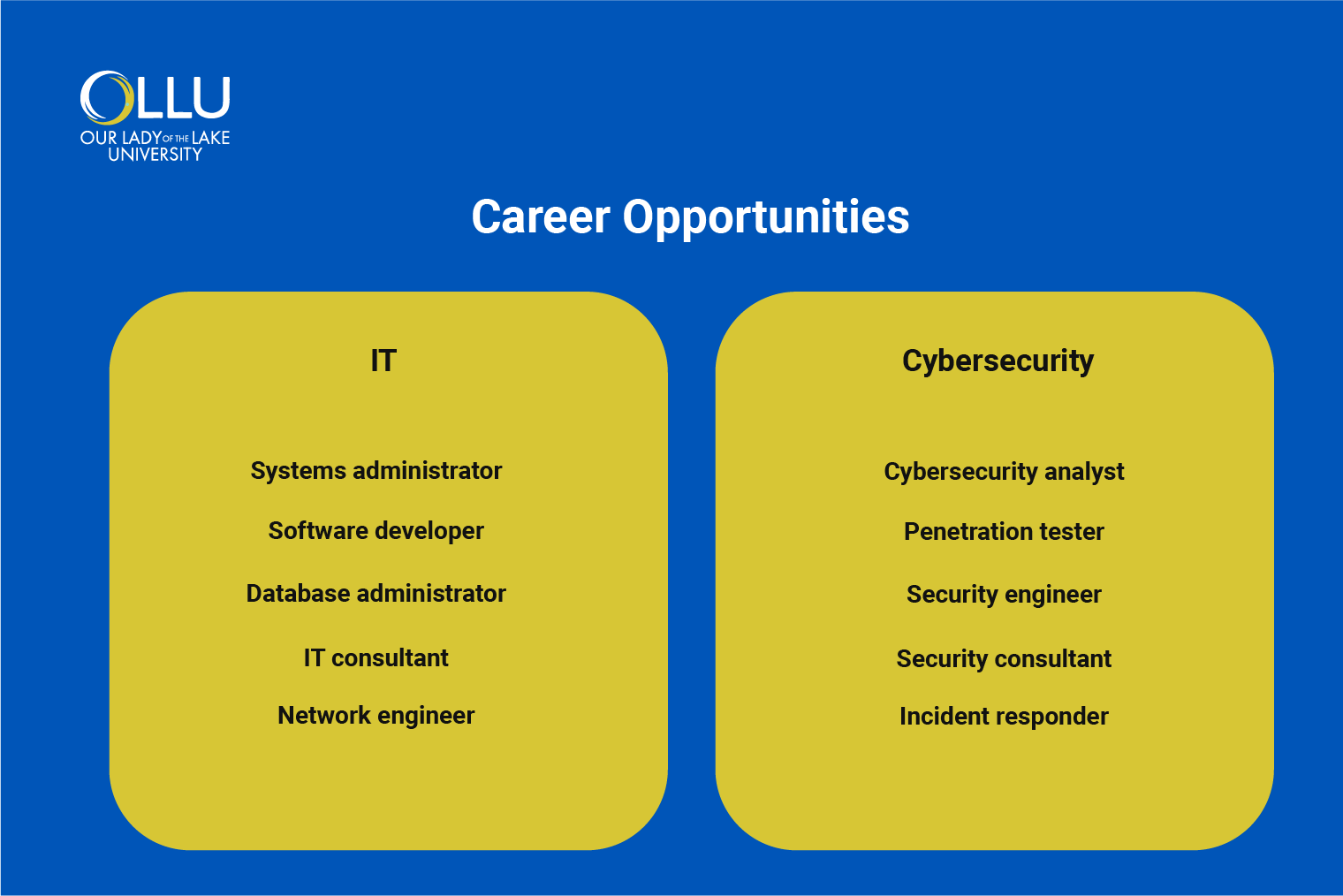
In the U.S., there are over 585,000 tech companies, providing abundant job opportunities in both IT and cybersecurity. This thriving industry offers a wide range of career options, some of which we’ll explore below.
IT
Firstly, graduates with an IT degree can pursue various roles in both technical and non-technical capacities. These roles may include:
- Systems administrator: Responsible for the configuration, maintenance and troubleshooting of hardware and software systems.
- Software developer: In charge of designing and creating applications, websites and software solutions to meet specific needs.
- Database administrator: Tasked with managing and optimizing databases, ensuring data integrity and availability.
- IT consultant: Provides expert advice on technology strategy, implementation and optimization for organizations.
- Network engineer: Responsible for designing, implementing and managing computer networks. They ensure network performance, security and availability.
- Business intelligence analyst: Responsible for gathering data and then utilizing data analysis tools and techniques to help organizations make informed business decisions.
- Cloud solutions architect: In charge of designing and implementing cloud-based solutions for organizations to optimize performance, security and cost-effectiveness.
- Cybersecurity consultant: Tasked with assessing vulnerabilities, recommending security measures and assisting in incident response and recovery.
- UX/UI designer: Responsible for creating user-friendly and visually appealing interfaces for websites, applications and software systems.
- IT project manager: In charge of overseeing the planning, execution and completion of IT projects as well as managing resources, budgets, timelines and ensuring that projects align with organizational goals.
Cybersecurity
Likewise, having a cybersecurity degree ensures your eligibility in various roles, including:
- Cybersecurity analyst: Responsible for monitoring and analyzing security incidents as well as implementing measures and response plans to enhance security.
- Penetration tester: Focused on simulating cyber-attacks to uncover vulnerabilities in systems, networks and applications.
- Security engineer: Responsible for designing and implementing security solutions like firewalls, encryption protocols and access controls.
- Security consultant: Responsible for advising organizations on best practices, conducting risk assessments and developing effective security strategies.
- Incident responder: In charge of investigating and mitigating security breaches, ensuring a swift and effective response to incidents.
- Security architect: Responsible for designing and constructing secure systems and networks, incorporating multiple layers of defense against cyber threats.
- Forensic analyst: Tasked with investigating cybercrimes, gathering evidence and contributing to legal proceedings.
- Security compliance analyst: Required to ensure an organization adheres to industry and regulatory compliance standards.
- Security director: Responsible for overseeing security programs, including policy development, risk management and incident response.
- Chief information security officer (CISO): Required to provide strategic leadership, manage security policies and ensure compliance with regulations.
It’s important to note that certain positions may necessitate specific certifications or degrees. Therefore, ongoing education and professional development are often critical for advancement in this field.
Skill Sets and Traits for Success
The right skills and traits are vital for success in IT, cybersecurity and any other field. The key is to have a skill set that enhances your abilities and helps you adapt to the fast-paced tech world. So, let’s explore what skills and traits you can develop through an IT and cybersecurity degree.
IT
IT degree programs aim to help you develop your technical proficiency as well as hone traits that enable you to adapt to the ever-evolving landscape of technologies and effectively collaborate with teams. Some of the skills and qualities necessary for success in the IT field include:
- Mastery of programming languages, operating systems and software applications
- Competency in network administration, cybersecurity and database management
- Efficient allocation of time and resources to meet project deadlines
- Willingness to explore new technologies and methodologies
- Skills to analyze problems and come up with creative solutions
- Precision in coding, system configuration and troubleshooting to ensure accuracy and reliability
- Ability to collaborate and work in teams, facilitating clear and efficient communication
- Adherence to ethical standards and practices in handling sensitive data and information
Cybersecurity
Similarly, cybersecurity degree programs can help equip you with a wide range of skills and traits that are crucial for success, such as:
- Effective communication and collaboration capabilities
- A comprehensive grasp of legal and compliance structures
- Knowledge of firewalls, intrusion detection systems and encryption protocols
- Upholding ethical integrity
- Proficiency in utilizing cybersecurity tools and technologies
- Skill in addressing security concerns, identifying vulnerabilities and devising strategic resolutions
- Competency in ethical hacking techniques and penetration testing
- Strong analytical and critical thinking abilities
Financial Considerations
Before choosing between any degree options, it is crucial to consider the financial aspect of each one, more specifically, the potential return on investment.
The cost of an IT or cybersecurity degree depends on the institution you choose and the format you pursue, with the average cost for a master’s degree being $65,134. With that in mind, data shows that cybersecurity professionals in the United States earn an estimated total pay of $101,800 per year, with salaries ranging from $60,000 to $174,000.
On the other hand, IT professionals make $93,614 per year, with the salary ranging from $74,000 to $119,000. In addition to that, both fields offer additional compensation through bonuses, benefits and potential for entrepreneurship.
All in all, the return on investment for both degree options is promising, as the yearly total pay you can expect is significantly higher than the average cost of a master’s degree.
Future Outlook
Both IT and cybersecurity offer highly favorable employment prospects in the swiftly advancing realm of technology. Recent data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) highlights the promising job outlook for computer and information technology professionals. Projections spanning from 2022 to 2032 predict a significant growth rate, exceeding the average for all occupations. It is anticipated that approximately 377,500 new job openings will arise annually in these domains.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Degree
Various factors can impact your educational journey and future career prospects. So, before you choose between IT, cybersecurity and any other degree program, consider the following factors:
- Program flexibility: Many higher education institutions provide different degree formats, such as full-time, part-time, online, on-campus and hybrid. For example, our esteemed online cybersecurity master’s program is renowned for its adaptability, allowing you to fit it into your schedule easily.
- Interests and goals: It is crucial to ensure that the degree and program you choose fits in with your long-term aspirations and aligns with your objectives, as well as is something you love doing.
- Job market: The insights gained from thorough research into the job market for your chosen field of study, especially in your specific region, can be crucial to ensuring you make the “right” decision.
- Education requirements: We recommend you review the educational prerequisites for the programs or roles that pique your interest, as they may necessitate specific prior degrees, majors or certifications.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, IT and cybersecurity offer promising career paths in today’s technology-driven world. So, if you’re drawn to the broader spectrum of IT or the specialized cybersecurity domain, the growth opportunities are abundant.
If you’re ready to embark on this exciting journey, consider joining our school. We offer outstanding undergraduate and master’s degree programs designed to equip you for the dynamic and ever-expanding world of technology. Explore your options and take the first step toward a rewarding career with us.
FAQ
Should I major in cybersecurity or IT?
The choice depends on your specific interests and career goals. If you enjoy protecting computer systems and handling cybersecurity, go for a major in cybersecurity, whereas if you prefer a more general view of technology, like software, networks and databases, a major in IT might be a better fit.
Which is better, cyber or IT?
Neither is objectively better than the other. Ultimately, it depends on your interests and career goals.
Is cybersecurity harder than IT?
The difficulty level between cybersecurity and IT can vary depending on individual strengths and interests. However, cybersecurity may be perceived as more challenging due to its specialized focus compared to IT, which is a broad field.