What Is Financial Risk Management? Strategies & Importance
Dec 04, 2024

-
Financial Risk Management involves the identification, analysis, and management of various types of risks, including market, credit, operational, liquidity, operational, and regulatory risks. The primary goal is to ensure financial stability and minimize potential losses for both individuals and organizations.
-
A career in financial risk management demands a strong educational background, certifications like the FRM, and technical proficiency in tools like Python and Excel.
-
Effective risk management strategies include risk avoidance, risk reduction, risk transfer, and risk retention.
Whether you’re a business owner or managing personal finances, it is important to protect your future by effectively managing financial risks. Financial risk management involves identifying, analyzing, and addressing potential financial losses to ensure stability and achieve long-term goals. Both businesses and individuals should apply a financial risk management approach to avoid economic setbacks, preserve profits, and secure financial stability. Below, we will explore different types of financial risks, management strategies, and career opportunities in the field of financial risk management.
What Is Financial Risk Management?
Financial risk management is the process of identifying and assessing potential risks that may impact a company’s investments and overall financial ability. In cases where potential risks are identified, professionals assess whether they have to accept or mitigate the risks. The risks can be qualitative or quantitative. For analyzing qualitative risks, professional judgment is required, whereas, for quantitative risks, the analysis is based on numerical or historical data.
Finance managers will use available financial tools to ensure the business is safe from any risks or, in financial terms, to hedge the business against them. The main goals of financial risk management include minimizing financial losses, maintaining financial stability, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
Types of Financial Risks
Finance executives need to consider several different types of financial risks before formulating or implementing investment strategies. These risks include market, credit, liquidity, operational, and legal & regulatory risks, each with specific features and objectives, which will be explored in more depth below.
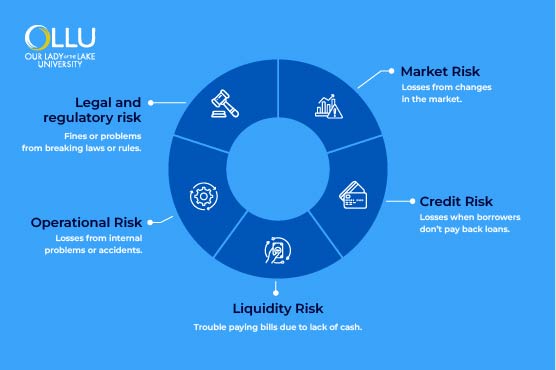
Market risk
Market risk refers to the likelihood of experiencing financial losses caused by changes in market conditions. These risks stem from broad economic uncertainties, such as industry-specific issues or geopolitical events that influence the economy. Factors contributing to market risks include changes in interest rates, fluctuations in currency exchange rates, volatility in stock markets, and major economic developments. These risks can significantly impact businesses, investors, and financial institutions, underscoring the importance of proactive monitoring and risk mitigation strategies.
Credit risk
Credit risk increases when a borrower is unable to repay loans or meet contractual deadlines and obligations, leading to potential financial losses. Common causes include borrower defaults, reduced business activity, and poor credit assessments. Credit risk can significantly impact financial institutions, investors, and the economy as a whole by causing financial losses and restricting the availability of credit.
Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk refers to the inability to fulfill short-term financial obligations as a result of having insufficient liquid assets available, which can disrupt business operations and threaten financial stability. These risks can be funding liquidity risks or market liquidity risks. The former occurs when an organization cannot secure sufficient funds to meet obligations, and the latter occurs when assets cannot be sold quickly without incurring heavy losses. Liquidity risks can also disrupt businesses' overall operations.
Operational risk
Failures in internal processes, people, systems, or external events that impact an organization's day-to-day operations may result in operational risks. Unlike market and credit risks, operational risks are internal to the organization and may be caused by human error, fraud, technology failures, cybersecurity breaches, or natural disasters. Consequently, the business can experience reputational damage, regulatory penalties, and operational disruptions.
Legal and regulatory risks
Legal and regulatory risks can occur as a result of legal actions, changes in regulations, or failure to comply with the law. These risks can cause financial penalties, operational challenges, and reputational harm. Failing to stay abreast of evolving regulations and ensure compliance can have severe long-term effects on business operations and credibility.
Financial Risk Management Process
The process of financial risk management is a structured action plan that financial analysts undertake to identify and address potential risks. This plan involves a series of steps: identifying potential financial risks, assessing their severity, and determining how they can be managed.
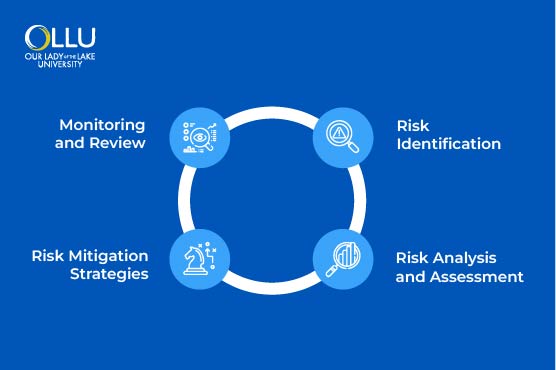
Risk identification
Risk identification and documentation is the initial step in the financial risk assessment process. Organizations can learn from past experiences, industry standards, and best practices to identify potential risks. Additionally, they should consider examining the company’s financial statements, disclosures, balance sheets, reports, and other relevant documentation. Financial assessors should focus on key areas, such as debt, expenses, liabilities, and cash flow, to ensure that all potential risks are recognized early in the process.
Risk analysis/assessment
Risk analysis is the second step, which evaluates the likelihood of a risk occurring and how it would affect the business. Risks can be prioritized by combining the probability score with the impact score, helping to determine which risks pose the greatest threat. The company should also consider its objectives, goals, and priorities before deciding which risks to address first.
Risk mitigation strategies
Risk mitigation strategies involve implementing processes and solutions to limit potential risks or minimize their impact if they occur. A mitigation plan aims at decreasing the risk score to a more manageable level for the company.
Monitoring and review
Finally, risk monitoring is the final step in the financial risk management process. Risk monitoring should be continuous and consistent in tracking the progress of risk mitigation strategies, updating the risk register, and using past experiences to improve the risk management procedure. Regular assessments should occur annually, with quarterly meetings held to discuss emerging financial risks. These evaluations help ensure that the company remains proactive in managing risks and demonstrates progress in achieving its financial management goals.
Strategies for Financial Risk Management
Today's economy can be unpredictable, making it necessary to develop strong risk management strategies. An efficient financial risk management strategy recognizes and reduces risks that could potentially lead to financial losses, protecting the company's overall financial health. Businesses can maintain their stability, make informed decisions, and plan for the long term simply by effectively managing risks. These strategies benefit both individuals and companies. Strategies include a four-stage process, including risk avoidance, risk reduction, risk transfer, and risk retention. Below, we will briefly explain each step.
-
Risk avoidance: Involves avoiding or eliminating activities that may expose individuals or organizations to financial risks or losses. On a personal level, they can avoid credit or debt risk by refraining from using credit to make purchases. For companies, this could mean choosing not to enter a new market with a high level of instability to avoid financial setbacks.
-
Risk reduction: Includes mitigating potential losses when risks do occur. For example, individuals or companies are advised to expand their investments instead of putting all their money into one investment to avoid losses if one investment does not perform well.
-
Risk transfer: Deals with transferring the responsibility for managing certain risks to a third party. They could purchase insurance policies that ensure protection against specific risks, such as medical expenses or property damage. By shifting the burden to an insurer, individuals and organizations maintain financial stability without fearing unexpected costs from large losses.
-
Risk retention: Involves accepting responsibility for specific risks when they occur. This could be used when individuals or companies choose to self-insure against smaller risks instead of buying an insurance policy. For example, companies may choose to cover the cost of low-value office equipment out-of-pocket if it gets damaged rather than paying for insurance coverage for those items. This approach is typically applied to risks that are less likely to result in significant financial losses.
Importance of Financial Risk Management
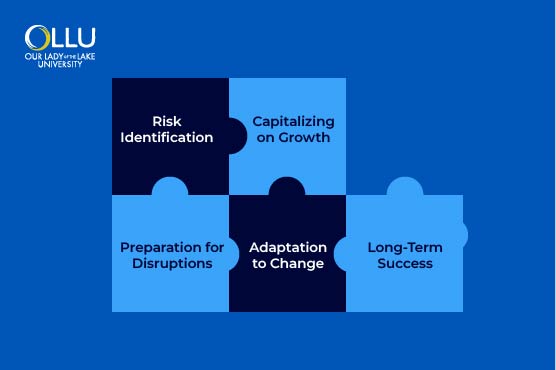
Financial risk management is important for companies aiming to safeguard assets and maintain stability in unpredictable situations. This procedure manages risks effectively to help businesses capitalize on growth opportunities while minimizing the negative impacts of financial losses. As new technologies and securities emerge, procedures for risk management must evolve to address evolving threats.
In addition, effective risk management prepares businesses for potential disruptions, such as economic downturns, operational failures, or natural disasters. Overall, financial risk management offers specific tools to companies to adjust to changes and seize opportunities, ensuring long-term success and resilience.
How to Build a Career in Financial Risk Management
A successful career in financial risk management requires a strong educational foundation, typically starting with an undergraduate degree in finance, economics, accounting, or business administration. These fields provide essential knowledge of financial principles, economic theories, and quantitative methods. Furthermore, if you want to advance your expertise, pursuing a Master’s in Risk Management or Financial Engineering can sharpen your skills in investment analysis and strategic decision-making.
Apart from education, certifications such as the Financial Risk Manager (FRM) designation from GARP demonstrate your proficiency in risk assessment, financial regulations, and risk mitigation strategies. A successful career in financial risk management also requires robust technical skills, such as proficiency in software like SAS or MATLAB, financial modeling, and data analysis tools such as Excel, Python, or R.
Conclusion
In conclusion, financial risk management is an important aspect of maintaining stability within a company. Whether you are working as an individual or as a company, you should follow the right procedures in managing your finances. This can be done by identifying, assessing, or minimizing risks such as market, credit, liquidity, operational, or legal risks.
This article highlighted strategies such as risk avoidance, risk reduction, risk transfer, and risk retention. In addition, we described the necessary steps for a successful career in financial risk management. You can build a rewarding career with the right education, certifications, and technical skills.
Explore programs offered by Our Lady of the Lake University in business or financial analysis to take the first step into the world of finance and business.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between financial risk management and enterprise risk management (ERM)?
Both financial risk management (FRM) and enterprise risk management (ERM) deal with risk management strategies. However, financial risk management only deals with risks that can affect the company’s financial stability. Enterprise risk management (ERM) focuses on all types of risks that an organization may face, including financial, operational, and strategic risks.
What are the top certifications for financial risk management professionals?
Financial risk management professionals demonstrate their knowledge and expertise by earning various industry-recognized certifications, including Professional Risk Manager (PRM), Chartered Enterprise Risk Analyst (CERA), Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC), Diploma in Risk Management, Certified Risk Management Professional (CRMP), Certified Risk and Compliance Management Professional (CRCMP), Certified Risk Manager (CRM), and Certification in Risk Management Assurance (CRMA).