Counselor vs Therapist: What You Need to Know to Decide
Dec 10, 2024
 This blog explains the differences between counselors and therapists. It explores
their roles, educational requirements, treatment approaches, and scopes of practice.
Understanding these differences is essential whether you are seeking assistance or
considering a career in the mental health field.
This blog explains the differences between counselors and therapists. It explores
their roles, educational requirements, treatment approaches, and scopes of practice.
Understanding these differences is essential whether you are seeking assistance or
considering a career in the mental health field.
Picture this: You’re feeling stressed and overwhelmed, and you know it’s time to talk to someone. You keep hearing about counselors and therapists and wonder, “What's the difference between a counselor and a therapist? Which one should I choose?"
Understanding the differences between these two roles is crucial, whether you are seeking support for yourself or contemplating a career in mental health. In this blog, we will break down the roles of counselors vs therapists, and explore key differences between the two.
What Is a Counselor?
A counselor is someone who helps people deal with challenges in their lives. They focus on specific issues and support clients in finding ways to cope. Counselors often work in schools, community centers, or private offices, helping with problems like grief, school difficulties, or making career choices.
They usually provide shorter-term help, which is great for people who need focused support. Counselors prioritize practical ways to handle problems and often use talk therapy to encourage communication and self-reflection.
They focus on actionable questions rather than theoretical ones, such as “How can we fix it?” or “What do we need to do to meet your needs?”. This type of counseling creates a safe environment for clients to understand their feelings. They might use techniques like cognitive-behavioral approaches to help clients shift negative thoughts into more positive ones.
What Is a Therapist?
A therapist provides a wide range of mental health services and often works with clients facing deeper psychological challenges. They use different techniques that are personalized to meet each person’s needs. Some common types of therapists include:
-
Clinical Psychologists
-
Marriage And Family Therapists
-
Licensed Social Workers
-
Psychotherapists
Therapists can provide treatments that deepen or complement traditional talk therapy,
such as:
-
Trauma-focused therapy
-
Marriage or relationship therapy
-
Psychoanalysis
-
Conflict resolution therapy
-
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
-
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
-
Dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT)
-
Psychodynamic therapy
They assess and diagnose mental health disorders and create long-term treatment plans that tackle the root causes of these issues.
Therapists use various methods, such as psychodynamic therapy, which looks at how our past experiences affect us, or dialectical behavior therapy, which focuses on skills like mindfulness and regulating emotions.
Counselors vs. Therapists: Key Differences
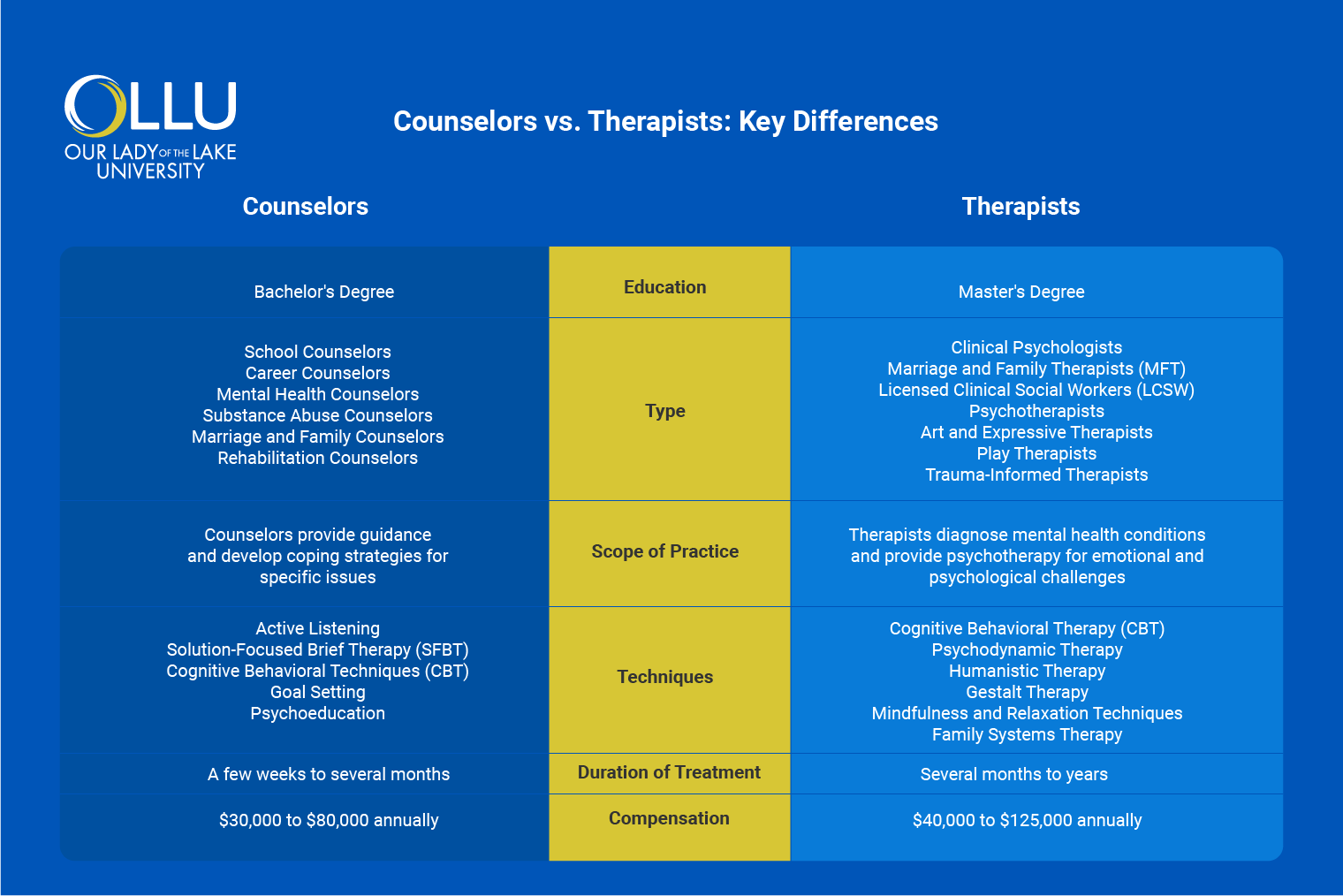 There are a few areas in which counselors and therapists differ. Let’s go through
them together.
There are a few areas in which counselors and therapists differ. Let’s go through
them together.
Educational Requirements
Both counselors and therapists generally follow similar educational paths, involving a bachelor’s and master’s degree, but therapists must pursue additional doctoral education and more specialized training.
For counselors, common majors include:
-
Bachelor of Human Services
-
Bachelor of Education
Whereas for a master’s degree, counselors should pursue:
-
Master of Counseling (MC)
-
Master of Education in Counseling (M.Ed)
For therapists, the requirements are generally more extensive. They need at least a master’s degree, such as:
-
Master of Social Work (MSW)
-
Master of Arts/Science in Psychology
-
Master of Marriage and Family Therapy (MFT)
-
Master of Clinical Mental Health Counseling
To become a therapist, you will need to pursue a doctoral degree such as a Doctor of Psychology (Psy.D.) or Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.).
Types of Counselors and Therapists
Counselors and therapists specialize in various aspects of mental health and personal development. Here is a breakdown of all the types of counselors vs therapists:
Types of Counselors
-
School Counselors
-
Work in educational settings to support students' academic, social, and emotional development
-
Focus on academic counseling, career guidance, and personal issues
-
-
Career Counselors
-
Help individuals assess their skills, interests, and values to make informed career choices
-
Provide guidance on job search strategies, resume writing, and interview preparation
-
-
Mental Health Counselors
-
Work with individuals dealing with mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and trauma
-
Use various therapeutic techniques to promote mental well-being
-
-
Substance Abuse Counselors
-
Specialize in helping individuals with addiction and substance use disorders
-
Focus on treatment plans, recovery support, and relapse prevention strategies
-
-
Marriage and Family Counselors
-
Address issues within relationships and families, such as communication problems and conflicts
-
Use systems theory to understand and resolve dynamics within family structures
-
-
Rehabilitation Counselors
-
Assist individuals with disabilities in achieving personal, social, and vocational goals
-
Work in settings like hospitals, rehabilitation centers, and community organizations
-
Types of Therapists
-
Clinical Psychologists
-
Hold a doctoral degree and provide psychotherapy, assessments, and psychological testing
-
Often focus on diagnosing and treating mental disorders
-
-
Marriage and Family Therapists (MFT)
-
Specialize in treating couples and families to improve relationships and resolve conflicts
-
Use techniques that address systemic issues affecting family dynamics
-
-
Licensed Clinical Social Workers (LCSW)
-
Provide therapy and support services, often focusing on social and environmental factors affecting mental health
-
Work in various settings, including hospitals, schools, and community agencies
-
-
Psychotherapists
-
General term for professionals who provide therapy; may include psychologists, counselors, and social workers
-
Use a range of therapeutic approaches to address emotional and psychological issues
-
-
Art and Expressive Therapists
-
Utilize creative modalities such as art, music, or dance to help clients express feelings and process experiences
-
Effective for individuals who may find traditional talk therapy challenging
-
-
Play Therapists
-
Work primarily with children using play as a medium for communication and expression
-
Help children process trauma, develop coping skills, and improve emotional regulation
-
-
Trauma-Informed Therapists
-
Specialize in treating individuals who have experienced trauma
-
Focus on creating a safe environment and using strategies to help clients process trauma
-
Scope of Practice
 The legal scope of practice also differs between counselors and therapists. Counselors
are generally permitted to provide guidance and develop coping strategies for specific
issues. They can conduct assessments for educational or career purposes but typically
do not diagnose mental health disorders.
The legal scope of practice also differs between counselors and therapists. Counselors
are generally permitted to provide guidance and develop coping strategies for specific
issues. They can conduct assessments for educational or career purposes but typically
do not diagnose mental health disorders.
Therapists have a broader scope, allowing them to diagnose mental health conditions and provide psychotherapy for emotional and psychological challenges. They employ various treatment modalities tailored to individual needs, addressing more complex issues than counselors typically do.
Approaches and Techniques
Counselors usually work with clients for a shorter period of time. They focus on teaching coping skills and providing support. Common counseling techniques include:
-
Active Listening: Fully engaging with the client to understand their concerns
-
Solution-Focused Brief Therapy (SFBT): Emphasizes finding solutions rather than exploring problems in depth
-
Cognitive Behavioral Techniques (CBT): Helps clients identify and change negative thought patterns
-
Goal Setting: Collaboratively setting achievable objectives to guide the counseling process
-
Psychoeducation: Providing information about mental health and coping strategies
On the other hand, therapists generally work with individuals or families over a longer time, offering more in-depth therapy sessions to help with deeper issues. They use techniques like:
-
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Focuses on changing unhelpful cognitive distortions and behaviors
-
Psychodynamic Therapy: Explores unconscious processes and past experiences to understand present behavior
-
Humanistic Therapy: Emphasizes personal growth and self-actualization; includes techniques like unconditional positive regard
-
Gestalt Therapy: Focuses on the present moment and awareness of feelings and actions
-
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Incorporates practices to help clients stay present and manage anxiety
-
Family Systems Therapy: Examines family dynamics and relationships to understand individual behaviors
Duration of Treatment
The duration of a treatment is largely based on the approaches, the issues being addressed, and the goals of the client.
Counseling sessions typically last a few weeks to several months, depending on the specific issue at hand. This shorter time frame makes counseling suitable for individuals seeking immediate support for specific life challenges (e.g., career change).
Therapy, however, can last several months to years. The length of treatment often depends on the complexity of the issues being addressed and the client’s progress. Some clients require ongoing therapy to work through deeper emotional challenges (e.g., PTSD, severe depression).
Compensation
Counselors' and therapists' salary ranges based on education, location, and experience. Counselors generally earn between $30,000 to $80,000 annually, with variations depending on their specialization and the settings in which they work.
Therapists tend to have a higher earning potential, with average salaries ranging from $40,000 to $125,000 per year. Those with advanced degrees or specialized training can earn more, especially in private practice or clinical settings.
Choosing Between a Counselor and a Therapist
Choosing between a counselor and a therapist can be hard, whether you're considering a career path or seeking personal treatment. Both roles offer unique opportunities to facilitate healing and growth, and each can lead to profound personal fulfillment.
To make your choice, reflect on your:
-
Career Goals: Determine whether you prefer to provide guidance and support for specific life issues (counseling) or explore deeper psychological processes (therapy).
-
Preferred Work Settings: Consider if you envision yourself in schools, community centers, or private practice, as these lean more toward counseling or therapy.
-
Client Demographics: Think of the populations you feel drawn to help—children, adolescents, adults, or families—and how that aligns with each role.
-
Training and Education: Research the educational requirements and training paths for both roles to find the best fit for your interests and commitment level.
-
Personal Fulfillment: Reflect on what brings you joy and satisfaction in helping others; this can guide you toward the most rewarding path.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between counselors and therapists is important if you're thinking about a career in mental health or looking for support. Counselors usually help with specific issues in a short amount of time, teaching coping strategies. Therapists focus more on deeper emotional and mental health problems and use a variety of methods to help. Both play important roles in healing and can be rewarding jobs.
If you're inspired to learn more, consider exploring the programs available at Our Lady of the Lake University, where you can embark on a fulfilling path toward becoming a counselor or therapist.
For more information, don't hesitate to contact us—your future in counseling or therapy awaits!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Which is better, counselor or therapist?
It depends on your needs. Counselors often focus on specific issues and provide guidance, while therapists may work on deeper psychological problems and provide long-term support.
Are there any online or remote options for counseling and therapy?
Yes, there are many online and remote options for counseling and therapy, including video calls, chat sessions, and apps that connect you with licensed professionals.
How often should I see a counselor or therapist?
It generally depends on your needs, but many people see a counselor or therapist weekly or bi-weekly. Some benefit from monthly sessions, while others might need more frequent visits during challenging times.